Muscular Sub-Category
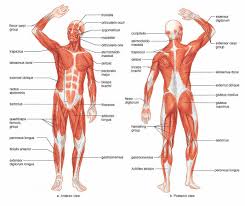 Muscular system is the system of Human Body that provides motor power for
Muscular system is the system of Human Body that provides motor power for
all movements of body parts. Muscular system is composed of special tissue
called muscular tissue. Muscles have the ability to contract actvely to provide
the force for movements of body parts. Muscular system is an important system
of human body because without it, life will completely stop. Muscles produce
not only those movements that are under the control of our will and that we
can see and feel, but also those movements that are responsible for activities
like breathing, digestion of food, pumping of blood etc.
Types Of Muscles:
Muscles:
Muscles are body tissues that provide the force for all body movements. They
are made of special types of cells. For details of structure and types of muscles,
please see the basic anatomy article. For details of microscopic structure of
muscles, pleas see the histology article.
Types of muscles:
Muscles are basically of three types; Skeletal Muscles, Smooth Muscles and
Cardiac Muscles.
Skeletal Muscles:
Skeletal muscles form most of the human body weight. They are under the control
of human will and all body movements occurring by our will are produced by skeletal
muscles. They are called skeletal muscles because they are almost always found
attached to the skeleton and produce movements in different parts of the skeleton.
Smooth Muscles:
Smooth muscles form the soft body organs like stomach, intestine, blood vessels
etc. They are not under the will of human beings and are responsible for unconscious
body activities like digestion of food. They are called smooth muscles because when
seen under the microscope, they do not have any striation in contrast to the other
two types of muscles.
Cardiac Muscles:
Cardiac muscles are exclusively found in human heart and no where else. They are
extremely strong and powerful muscles. They are not under the control of human will
and are involuntary. The pumping of blood by human heart is because of the force provided
by the contraction of cardiac muscles.
 Muscular system is the system of Human Body that provides motor power for
Muscular system is the system of Human Body that provides motor power for